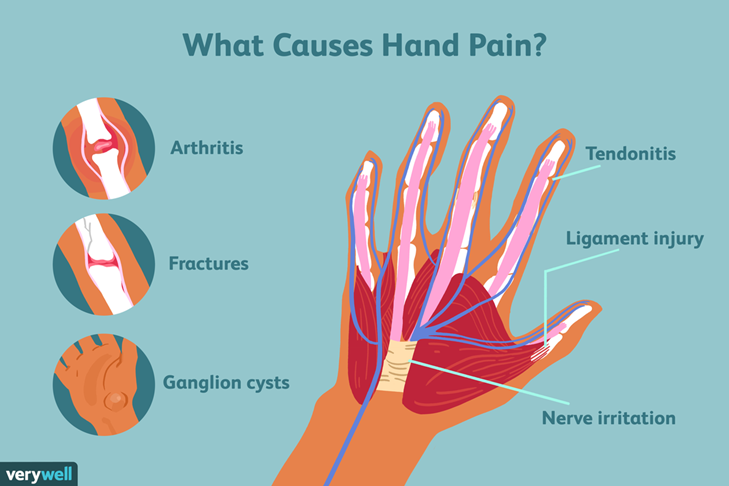
Finger joint pain is a frequent complaint that can affect anyone—young or old. From temporary discomfort to chronic conditions, finger pain can interfere with everyday tasks like writing, gripping, or typing. Understanding the common causes can help in early diagnosis and effective management.
Why Do Finger Joints Hurt?
The fingers are made up of small joints, tendons, ligaments, nerves, and bones that work together to allow movement and dexterity. When one or more of these structures are affected due to injury, overuse, or disease, it can result in joint pain.
Common Causes of Finger Joint Pain
1. Osteoarthritis
- What it is: A degenerative joint disease where the cartilage wears down over time.
- Symptoms: Stiffness, swelling, pain during movement, and bone spurs.
- Most affected: Older adults or people with a history of joint overuse.
2. Rheumatoid Arthritis
- What it is: An autoimmune condition where the immune system attacks the joint lining.
- Symptoms: Pain, swelling, warmth, stiffness (especially in the morning), and deformity over time.
- Most affected: Women and those with a family history of autoimmune disease.
3. Gout
- What it is: A form of inflammatory arthritis caused by uric acid crystal buildup.
- Symptoms: Sudden severe pain, redness, swelling, often starting in the big toe but can affect fingers.
- Triggers: High-purine diet (red meat, seafood), alcohol, or kidney dysfunction.
4. Injury or Trauma
- Examples: Sprains, fractures, or dislocations of the finger joints.
- Symptoms: Immediate pain, swelling, bruising, and limited motion.
- Most affected: Athletes, manual laborers, or those who fall on outstretched hands.
5. Tendinitis or Tenosynovitis
- What it is: Inflammation of tendons or their sheath due to overuse or repetitive motion.
- Symptoms: Aching, burning sensation, pain while moving the finger.
- Risk factors: Repetitive tasks (e.g., typing, texting), poor ergonomics.
6. Trigger Finger (Stenosing Tenosynovitis)
- What it is: A condition where a finger gets stuck in a bent position and then snaps straight.
- Symptoms: Clicking or locking sensation, tenderness at the base of the finger.
- Most affected: Middle-aged women, diabetics, and people with arthritis.
7. Infections
- What it is: Bacterial infections such as felon, paronychia, or septic arthritis can cause finger joint pain.
- Symptoms: Redness, warmth, swelling, pus formation, fever in severe cases.
- Urgency: Needs immediate medical attention to prevent joint damage.
8. Dupuytren’s Contracture
- What it is: A thickening of the fascia (connective tissue) in the palm, causing fingers to curl inward.
- Symptoms: Painless early on, progresses to difficulty in finger extension.
- Most affected: Men over 50, especially those with a family history or alcohol use.
Other Less Common Causes
- Psoriatic arthritis
- Lupus
- Neurological issues (e.g., pinched nerves in the neck)
- Hormonal changes (especially in menopausal women)
When to See a Doctor
Seek medical attention if:
- Pain persists more than a week
- Swelling or redness worsens
- You experience fever or signs of infection
- Joint movement becomes limited or locked
- Numbness or tingling occurs
Managing and Preventing Finger Joint Pain
Home Care Tips:
- Rest the fingers when overused
- Use cold compresses for swelling or hot compresses for stiffness
- Practice stretching and finger mobility exercises
- Use ergonomic tools and typing posture
Medical Options:
- Over-the-counter pain relievers
- Anti-inflammatory medications
- Corticosteroid injections
- Splints or braces
- Surgery in severe or advanced cases
Conclusion
Finger joint pain can stem from a wide range of causes—from everyday wear and tear to chronic inflammatory diseases. While mild pain may improve with rest and home care, persistent or severe symptoms should not be ignored. Early diagnosis and treatment are key to preserving hand function and quality of life.
Disclaimer: This blog is for educational purposes only and does not replace professional medical advice. Consult a healthcare provider for accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment.