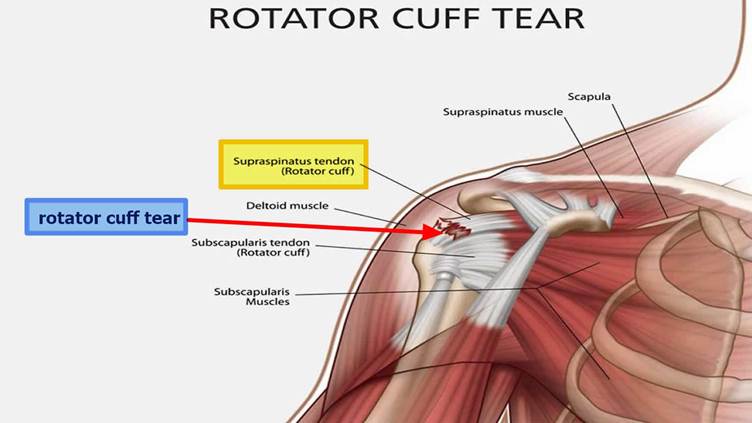
The rotator cuff is a group of muscles and tendons that stabilize the shoulder and allow it to move. An injury to the rotator cuff can lead to pain, weakness, and reduced mobility, affecting daily activities like lifting, dressing, or even sleeping.
Rotator cuff injuries are common, especially in athletes, older adults, and people with repetitive shoulder use. Understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and seeking proper treatment are essential for recovery.
What Is a Rotator Cuff Injury?
A rotator cuff injury occurs when one or more of the tendons in the shoulder become irritated, inflamed, or torn. Injuries may range from mild inflammation (tendinitis) to partial or complete tears of the tendons.
Types of Rotator Cuff Injuries
- Tendinitis: Inflammation of the rotator cuff tendons due to overuse.
- Bursitis: Inflammation of the bursa (a fluid-filled sac) that cushions the tendons.
- Tears:
- Partial tear: The tendon is damaged but not completely severed.
- Full-thickness tear: The tendon is completely torn and may pull away from the bone.
Common Causes of Rotator Cuff Injury
- Repetitive overhead motions (e.g., athletes, painters, carpenters)
- Lifting heavy objects or sudden trauma
- Falling on an outstretched arm
- Degeneration with age (more common after 40 years)
- Poor posture and muscle imbalance
Signs and Symptoms
- Persistent dull ache in the shoulder
- Pain that worsens when sleeping on the affected side
- Weakness in the arm, especially when lifting or rotating
- Difficulty reaching behind the back
- Clicking or popping sounds during shoulder movement
- Limited range of motion
Diagnosis
Diagnosis includes a physical examination, review of medical history, and imaging tests such as:
- X-rays: Rule out bone abnormalities.
- Ultrasound: Visualizes soft tissues like tendons.
- MRI: Most accurate test to determine the extent of tendon damage.
Treatment Options
Non-Surgical Treatments
These are usually the first line of management:
1. Rest and Activity Modification
- Avoid activities that worsen pain.
- Limit overhead and heavy lifting motions.
2. Medications
- Steroid injections for severe inflammation.
3. Physical Therapy
- Exercises to strengthen shoulder muscles and improve range of motion.
- Stretching to reduce stiffness and maintain flexibility.
4. Cold and Heat Therapy
- Ice reduces inflammation after activity.
- Heat relaxes tight muscles before exercises.
Surgical Treatments
Surgery is considered when:
- Non-surgical treatment fails after 6 months.
- There’s a complete tear or severe weakness.
- The tear is acute and caused by injury in younger individuals.
Surgical Options:
- Arthroscopic tendon repair: Minimally invasive, repairs torn tendons.
- Open tendon repair: Traditional method for large or complex tears.
- Tendon transfer: Used when tendons are too damaged to repair.
- Shoulder replacement: In severe or degenerative cases.
Rehabilitation and Recovery
Recovery can take 4 to 6 months, depending on the injury and treatment method:
- Early Stage: Pain control and gentle movement.
- Mid Stage: Gradual strengthening and flexibility exercises.
- Late Stage: Return to normal activity and sports-specific training.
Adherence to physical therapy is key to regaining function.
Prevention Tips
- Warm up before physical activity.
- Strengthen shoulder muscles with regular exercise.
- Avoid repetitive overhead motions or take breaks.
- Use proper lifting techniques.
- Maintain good posture.
Conclusion
Rotator cuff injuries can significantly affect your quality of life if left untreated. With early diagnosis, proper care, and commitment to rehabilitation, most individuals recover well. Always seek medical advice if shoulder pain or weakness persists.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult a healthcare provider for diagnosis and treatment.